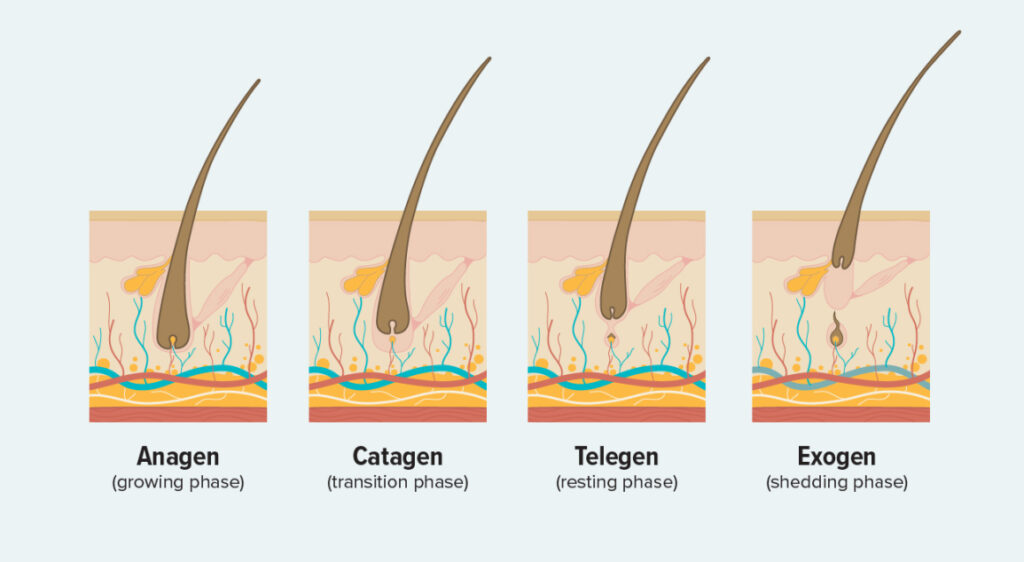
Stages of Hair Growth
- Anagen – growth phase (3-5 years sometimes 7)
- Catagen – regression phase (10 days)
- Telegen – resting phase (3 months)
What Causes Hair Loss
DHT is the hormone behind hair loss. It stands for Dihydrotestosterone and a build up of this androgen can cause permanent hair loss. High levels of androgens, including DHT, can shrink your hair follicles as well as shorten the hair cycle, causing hair to grow out looking thinner and more brittle, as well as fall out faster. DHT can also make it take longer for your follicles to grow new hairs once old hairs fall out.
How to reduce DHT
There are plenty of medications for DHT-related hair loss, and many of them have been proven effective by specifically targeting DHT production and receptor binding. There are two main types:
- Blockers. These prevent DHT from binding to 5-AR receptors, including those in your hair follicles that can allow DHT to shrink follicles
- Inhibitors. These reduce your body’s production of DHT
Hair Growth Medications
Finasteride
Finasteride (Proscar, Propecia) is an oral, prescription-only medication. It’s documented as having at least an 87 percent success rate with few noted side effects.
Finasteride binds to 5-AR proteins to block DHT from binding with them. This helps keep DHT from binding to receptors on your hair follicles and keeps them from shrinking.
Minoxidil
Minoxidil (Rogaine) is known as a peripheral vasodilator. This means that it helps widen and loosen blood vessels so that blood can more easily pass through.
It’s typically used as a blood pressure medication. But minoxidil can also help promote hair growth when it’s applied topically to your scalp.
Biotin
Biotin, or vitamin H, is a natural B vitamin that helps turn some of the food and liquids you consume into energy your body can use.
Biotin also helps boost and maintain levels of keratin, a type of protein present in your hair, nails, and skin. You can take biotin as an oral supplement, but it’s also present in egg yolks, nuts, and whole grains.
